Class 10, NCERT (CBSE) Science - Physics
LIGHT - REFLECTION AND REFRACTION
Physics (Science) Important Notes and Study Materials
(LESSON 2 of 3)
Mirrors
Formula
There is a
relationship between the distance of image (v), distance of object (u) and the
focal length of a spherical mirror (f) which is given by the Mirror Formula.
The mirror formula is,
Magnification
The
magnification of a spherical mirror gives the relative extent to which the
image of an object is magnified with respect to the object size. It is
expressed as the ratio of the height of image to the height of object.
The equation
holds true for both concave and convex mirror. M is –ve for inverted image and
+ve for erect image. So, magnification is always positive for a convex mirror,
while it depends on the position of the position of the object with respect to
concave mirror.
Refraction
The phenomenon
of bending of light as it travels from one medium to another medium is called
refraction of light.
When light
enters from a rarer medium into a denser medium it will bend towards the
normal. Similarly when light gets into a rarer medium from a denser medium it
will bend away fro the normal.
Refraction or
change in the direction in the light ray (bending) takes place on account of a
change in the speed of light on entering the second media. (Why does the phenomenon of refraction takes place? or, Why does the ray of light change the
direction when entering from one medium to another medium?)
Laws of Refraction
There are two laws of refraction:
(i) The incident ray, the refracted ray
and the normal to the interface of the two media at the point of incidence -
all lie in the same plane.
(ii) The ratio of the sine of the angle
of refraction for a given pair of media is constant. This is known as Snell’s
Law. Mathematically this can be represented as:
Refractive Index
It is the ratio of the angle of
incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction when light is refracted from
one medium to another medium. Refractive index is also linked to an important
physical quantity i.e. the relative speed of propagation of light in different
media.
Consider a ray o light travelling from
medium 1 (air) into medium 2 (glass) as shown in the above figure. Let v1
be the speed of light in the medium 1 and v2 in medium 2. The
refractive index of medium 2 with respect to medium 1 can be expressed as
n21 = (Sin i ÷ Sin
r) = (v1 ÷ v2)
Spherical Lens
A lens is a curved piece of glass or
any other transparent material bound by two surfaces of which one or both
surfaces are spherical, through which light can pass. There are two types of lenses:
Concave Lens and Convex Lens.
Concave Lens
A concave or bi-concave lens is made by
joining two curved surfaces in such a way that it is thinner at the center. The
thickness gradually increases as we move towards edge.
Convex Lens
A convex or bi-convex lens is made by
joining two curved surfaces in such a way that it is thicker at the center. The
thickness gradually reduces as we move towards the edge.
Optical Center
Optical center is a point at the center
of the lens. It lies inside the lens and not on the surface. Optical center is
usually represented by the letter O (as shown in the figures). a ray of the
light through the optical center of a lens always passes without suffering any
deviation.
Center of Curvature of a
Lens
It is the center point of arcs of the
two spheres from which the given spherical lens (concave or convex) is made.
Since a lens constitutes two spherical surfaces, it has two centers of
curvature.
Radius of Curvature of a
Lens
The distance of the optical center from either of the center of
curvatures is termed as radius of curvature.
Principal Axis of a Lens
An imaginary straight line passing
through the two centers of curvature of a lens is called its principal axis.
Power of a Lens
The degree of convergence or divergence
of light rays achieved by a lens is expressed in terms of its power (P). The
power of a lens is defined as the reciprocal of its focal length.
Cbse Ncert Guide Class 10 Physics Notes, Study Materials (Light - Reflection and Refraction):
- Cbse Guide Class 10, Science (Physics) | Light - Reflection And
Refraction | Solutions of Ncert Science In-Text Questions (to be published)
- Class 10, Solutions of Ncert Cbse Science (Physics) | Light - Reflection and Refraction (CCE type Multiple Choice Questions MCQs Solutions) (to be published)


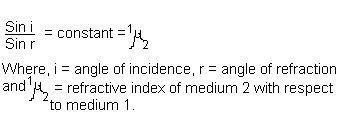





No comments:
Write comments